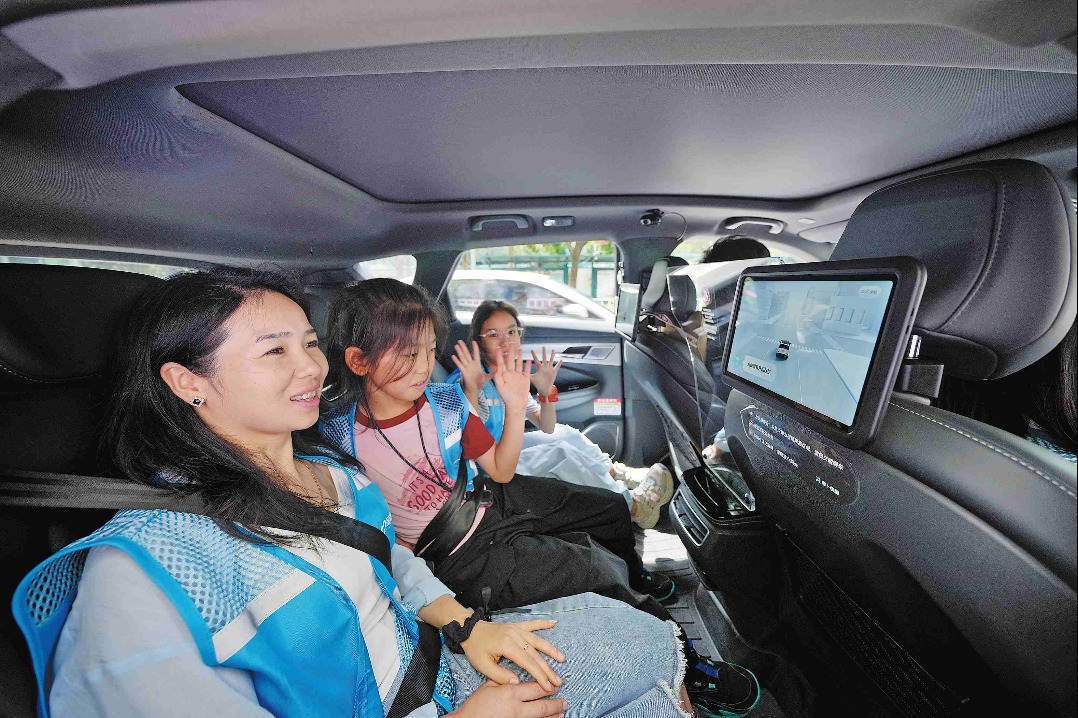
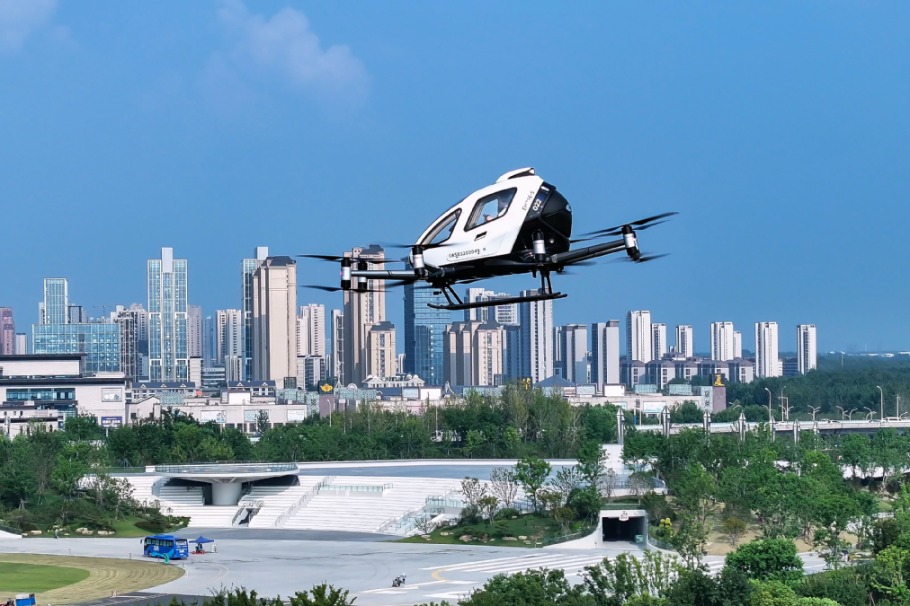
China's autonomous driving tech forges inroads into global markets
From Luxembourg to Dubai, domestically developed robotaxis are expanding their reach


Chinese self-driving startup WeRide is another company accelerating its global expansion, with the Middle East seen as a strategic priority for autonomous driving growth and innovation.
It is cooperating with Dubai authorities and Uber under an agreement, pilot operations of autonomous vehicles will commence later this year via the Uber app in Dubai. In the initial phase, the vehicles will operate with a safety driver on board, paving the way for the full-scale commercial rollout of driverless services in 2026.
In May, the company and Uber further expanded their partnership to roll out robotaxis in 15 additional major global cities over the next five years, including some in Europe. It has launched fully driverless robotaxi testing in Abu Dhabi, and other cities in the Middle East are being explored for testing.
The company is expanding into Saudi Arabia and has rolled out testing or deployment of its robotaxis in cities including Riyadh, setting the stage for commercial rollout and wider operations across the Middle East's largest economy.
WeRide's robotaxis support Saudi Arabia's push to develop a smart, sustainable transportation infrastructure for both residents and the rising influx of visitors.
Open to innovation
The scale of the global robotaxi market is expected to reach $45.7 billion by 2030, rapidly expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 91.8 percent from 2023 to 2030, data from research company MarketsandMarkets shows.
The growth of the robotaxi market is influenced by rising demand for ride-hailing services, high R&D investment and government focus on reducing emissions, infrastructure development, and growth of electric vehicles, according to the consultancy.
The need for robotaxis is also being fueled by the growing emphasis on sustainability, requirements for effective urban transit, and increased safety as a result of the abolition of human mistakes, it added.
At present, governments around the world are continuously introducing favorable policies to support the development of autonomous driving technology — including test permits and infrastructure construction — which is conducive to accelerating the application and popularization of the technology, according to WeRide.
Zhu Keli, founding director of the China Institute of New Economy, said the open, innovative environment and supportive policy measures for autonomous driving technology in some countries, especially the UAE and Luxembourg, provide Chinese self-driving companies with ideal testing sites and a broad development space.
"Their accelerated global expansion will bolster the maturity of autonomous driving technology, propel the deeper integration of global industrial chains, optimize resource allocation and inject fresh impetus into the development of the self-driving sector worldwide," Zhu said.
The accelerated international push of Chinese self-driving companies is inevitable in the face of increasingly fierce competition, said Duan from the School of International Trade and Economics at the Central University of Finance and Economics.
By cooperating with leading overseas companies, they can receive funding and policy support abroad and enhance their competitiveness in the global intelligent automotive sector. This will in turn drive the development of domestic companies involved in the autonomous driving industrial chain, she added. "Self-driving technology is expected to become an important field for China to share its development dividends with the world," Duan said.
Market consulting firm McKinsey& Company has forecast that China will become the world's largest market for self-driving vehicles, with revenue from such vehicles and mobility services exceeding $500 billion by 2030.
China has caught up with the US in developing autonomous driving, said Lyu Jinghong, an intelligent mobility analyst at research company BloombergNEF.
Lyu said ongoing testing on public roads, regulatory backing and cost reductions in autonomous vehicle manufacturing, will help accelerate the deployment and commercialization of self-driving cars.
However, Chinese self-driving companies' greater presence abroad may encounter some challenges, such as differences in culture, laws and regulations, she said. Lyu called for greater efforts to conduct testing based on different road conditions abroad, and improving knowledge about the usage habits of local consumers, as well as strengthening compliance and personal privacy protection.
Li Xinbo, an automotive industry analyst at China Auto Information Technology (Tianjin) Co, said as the operating costs and compliance risks in overseas markets are relatively high, Chinese enterprises need to carefully assess and formulate strategic plans, speed up localization efforts and launch services that cater to local requirements, when carrying forward their globalization push.