Scientists create the most detailed 3D map of a mouse brain

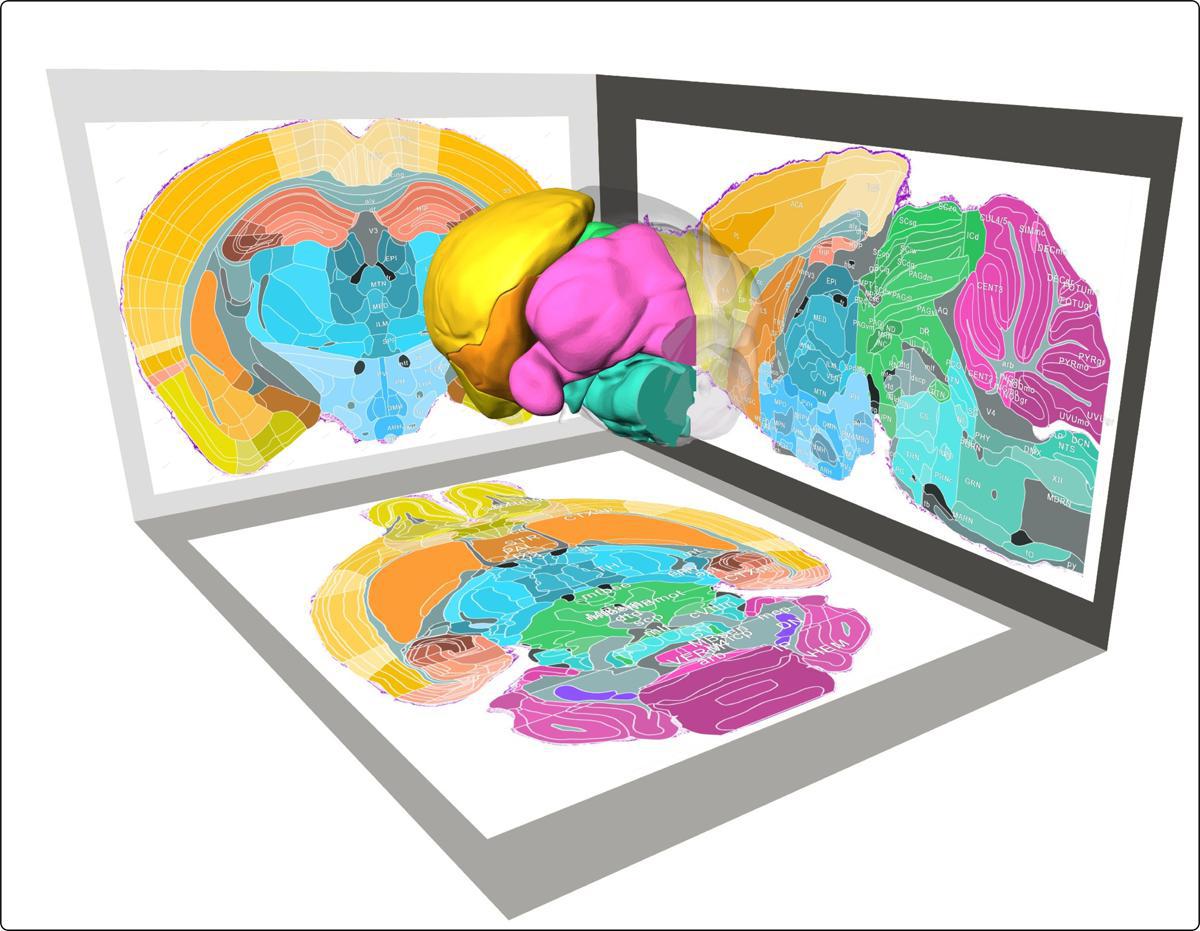
Scientists have created the most detailed 3D map of a mouse brain ever produced, a milestone that could revolutionize research on brain disorders, neural circuits, and even future surgical precision. The study, published in the prestigious journal Nature on Tuesday, offers a resolution so sharp that it can pinpoint structures as tiny as 1 micrometer — about one-fiftieth the width of a human hair.
Led by a team from Hainan University and the Huazhong University of Science and Technology in China, along with collaborators from the University of California, Los Angeles, the project overcomes longstanding limitations in brain mapping.
Traditional brain atlases were often blurry, two-dimensional snapshots with gaps between slices. The new stereotaxic topographic atlas of the mouse brain (STAM), however, provides a seamless, three-dimensional view at cellular-level precision.
"This is like upgrading from a paper road map to a live, interactive GPS for the brain," said academician Luo Qingming, co-lead researcher and president of Hainan University. "You can zoom in, rotate, and even 'dissect' regions digitally to study connections between neurons or blood vessels."
Brain atlases are essential tools for neuroscientists, much like anatomical guides for doctors. They help researchers navigate the brain's complex structures, track diseases, or test experimental treatments. But until now, even the best references — such as the widely used Allen Institute's mouse brain atlas — lacked the resolution to show individual cells clearly in all dimensions.
The stereotaxic topographic atlas changes that. Using a custom-built imaging system called Micro-Optical Sectioning Tomography, the team scanned over 34,000 ultra-thin slices of a mouse brain, stained to highlight cellular details. The result is a "Lego-like" digital model that labels 916 brain regions - 236 of them newly identified — with unprecedented clarity.
Mice are critical in biomedical research because their brains share about 90 percent of their genes with humans. Insights from mouse studies often pave the way for understanding human conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, or depression.
To ensure global access, the team built an open and free online platform where researchers and curious members of the public can explore the atlas, download data, or even simulate brain surgeries. The system also aligns with traditional brain maps, easing the transition for labs worldwide.
International experts hailed the work. Doctor Javier de Felipe of Spain's Cajal Institute called it "a highly significant achievement", while Australian neuroscientist George Paxinos — whose own mouse atlases are lab staples — praised the "unprecedented" data quality.
The team aims to expand the stereotaxic topographic atlas' applications, from testing drugs to guiding brain-machine interfaces. Luo also highlighted Hainan province's unique resources: "With our primate research resources, this work could bridge mouse studies to human brain exploration."
"While we've mapped distant galaxies, the human brain remains one of science's final frontiers," Luo said. The stereotaxic topographic atlas now bridges this gap, proving how microscopic breakthroughs - down to a single micron — can illuminate humanity's most complex organ.
- Scientists create the most detailed 3D map of a mouse brain
- Workers' federation allocates 40 million yuan for heat alleviation measures
- Human resources companies urged to cut dishonest practices, follow laws
- Giant pandas celebrate birthday party in Guangxi
- Former national legislator sentenced to life for bribery
- Yantai wine soars from fine vintages to lifestyle craft